Types of Furnace
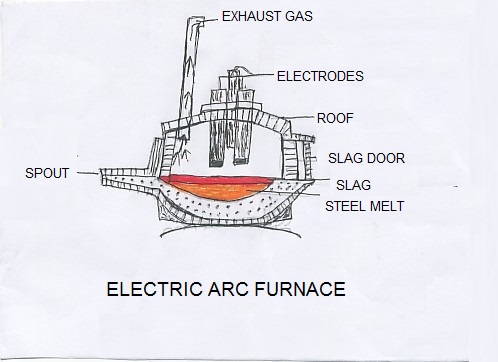
The electric arc furnace uses three carbon electrodes which dip into the charges. The lining is both acid and basic depending upon the nature of charge. If the charge is basic in nature, the linings of dolomite bricks are used. In case of acidic charge, silica bricks are used. The electric arc furnace is used for production of ferroalloys, plain carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel and heat-resistant steel. This process is expensive and the output is small. The average capacity of this furnace may vary from 100 kg to 100 tones per day. The electric arc furnace consists of steel shell lined with refractory bricks and removable roof. Through the roof, carbon or graphite electrode passes into the charge.
The electrodes are placed into the furnace and the current is passed into the electrodes. Heat generated by spark between the electrodes and the metallic charge melts the charge. The charge usually consists of scrap and sponge iron. Sometimes molten pig iron is also added to help slag formation. For removal of impurities and oxygen, ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, limestone and iron ore are added. The melt is produced in 6-8 hours. After the melt is produced, the refining is started by blowing of oxygen into the furnace. After sometime, the impurities along with the limestone form the slag and come to the top of molten bath. After the formation of the slag, the slag is slowly removed and transported to the slag pit. The process of refining may be repeated for sometime. As the refining is found to be complete, the molten steel is removed through the ladle and further to the casting pits. After the steel is cooled down in the casting pit, it may be quenched by pouring of cold water. Then the steel is ready for commercial use.
This furnace is in use where availability of coking coal and iron ore is negligible. The electric arc furnace is viable when the availability of power is in plenty and the cost of production is very low. This furnace has some advantages. The chemical conditions are clean and possibility of contamination of the steel is negligible. The removal of phosphorus and sulphur is found to be maximum in this furnace. The carbon content can be controlled properly. The addition of alloying elements like ferromanganese and ferrosilicon can be adjusted properly. ssThe control of temperature is also carried out accurately. The electric arc furnaces are used in small and medium scale steel plants.
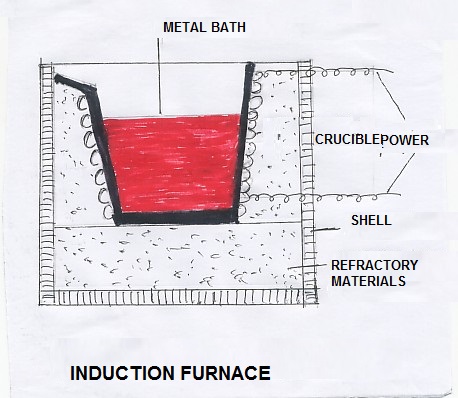
INDUCTION FURNACEThe induction furnace is developed for reducing the cost of power consumption. The principle of induction furnace resembles like the principle of a transformer. It has a primary coil through which an alternating magnetic field is set up. When alternating current is passed through the coil, a magnetic field is produced. This magnetic field induces eddy current in the circuit which comprises a crucible containing the metal charge. The eddy current provides the heat for melting the charges. The induction furnace comprises a refractory crucible and inductor. The inductor is made of copper tubes. An insulating lining is provided between the coil and the crucible. The charge materials are scrap and sponge iron. Addition of ferroalloys and limestone is also done before the melting. Heavy secondary current is induced by the magnetic field and heat is generated. The charge is melted and small amount of slag is formed above the top of the hot metal. The slag is separated through tilting the furnace. The steel melt is further separated through ladle and casting pits. This furnace is available in capacity between 15kg-10 tones. Refining is not possible in this furnace, but only melting is possible in it. So, a very clean charge should be used in this furnace.